SpringBoot整合Thymleaf实现页面静态化
1. 问题需求分析
- 在做乐优商城时,页面是通过Thymeleaf模板引擎渲染后返回到客户端。当商品详情页数据渲染时,在后台需要大量的数据查询,而后渲染得到HTML页面。在用户访问量大的情况下会对数据库造成压力,并且请求的响应时间过长,并发能力不高。
如何解决?
- 一般我们优先会考虑使用缓存技术,比如 Redis 分布式缓存,Guava 本地缓存等。然而 Redis 只适合数据规模比较小的情况,假如数据量比较大,例如商品详情页,每个页面如果10kb,100万商品,就是10GB空间,对内存占用比较大。此时就给缓存系统带来极大压力,如果缓存崩溃,接下来倒霉的就是数据库了。
- 所以缓存并不是万能的,某些场景需要其它技术来解决,比如静态化技术。
2. 什么是静态化?
- 静态化是指把动态生成的HTML页面变为静态内容保存,以后用户的请求到来,直接访问静态页面,不再经过服务的渲染。
- 而静态的HTML页面可以部署在nginx中,从而大大提高并发能力,减小tomcat压力。
3. 如何实现静态化?
目前,静态化页面都是通过模板引擎来生成,而后保存到nginx服务器来部署。常用的模板引擎比如:
- Freemarker
- Velocity
- Thymeleaf
乐优项目中使用的是Thymeleaf 模板引擎!
4. Thymeleaf实现静态化
4.1 概念介绍
Thymeleaf 模板引擎实现页面静态化的几个概念介绍:
- Context:运行上下文
- TemplateResolver:模板解析器
- TemplateEngine:模板引擎
Context:
Thymeleaf 模板中的上下文: 用来保存模型数据,当模板引擎渲染时,可以从Context上下文中获取数据用于渲染。
当与Spring Boot结合使用时,我们放入Model的数据就会被处理到Context,作为模板渲染的数据使用。
TemplateResolver:
Thymeleaf 模板中的模板解析器:用来读取模板相关的配置,例如:模板存放的位置信息,模板文件名称,模板文件的类型等等。
当与SpringBoot结合时,TemplateResolver已经由其创建完成,并且各种配置也都有默认值,比如模板存放位置,其默认值就是:templates。比如模板文件类型,其默认值就是html。
TemplateEngine:
Thymeleaf 模板中的模板引擎:用来解析模板的引擎,需要使用到上下文、模板解析器。分别从两者中获取模板中需要的数据,模板文件。然后利用内置的语法规则解析,从而输出解析后的文件。来看下模板引擎进行处理的函数:
1
| templateEngine.process("模板名", context, writer);
|
三个参数:
- 模板名称
- 上下文:里面包含模型数据
- writer:输出目的地的流
在输出时,我们可以指定输出的目的地,如果目的地是Response的流,那就是网络响应。如果目的地是本地文件,那就实现静态化了。
而在SpringBoot中已经自动配置了模板引擎,因此不需要关心这个。我们做静态化,就是把输出的目的地改成本地文件即可!
4.2 具体实现
GoodsHtmlService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
@Service
public class GoodsHtmlService {
@Autowired
private TemplateEngine templateEngine;
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
public void createHTML(Long spuId) {
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariables(goodsService.loadData(spuId));
File file = new File(
"M:\\note\\MyProjects\\leyou\\tools\\nginx-1.14.0\\html\\item\\" + spuId + ".html");
PrintWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new PrintWriter(file);
templateEngine.process("item", context, writer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (writer != null) {
writer.close();
}
}
}
public void asyncExcute(Long spuId) {
ThreadUtils.execute(() -> createHTML(spuId));
}
}
|
多线程工具类ThreadUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class ThreadUtils {
private static final ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void execute(Runnable runnable) {
es.submit(runnable);
}
}
|
GoodsController
在调用GoodsController访问商品页面的同时生成缓存的页面:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
@Controller
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
@Autowired
private GoodsHtmlService goodsHtmlService;
@GetMapping("/item/{id}.html")
public String toItemPage(@PathVariable("id") Long id, Model model) {
Map<String, Object> map = goodsService.loadData(id);
model.addAllAttributes(map);
goodsHtmlService.asyncExcute(id);
return "/item";
}
}
|
注意:生成html 的代码不能对用户请求产生影响,所以这里我们使用额外的线程进行异步创建。
5. nginx 中进行访问配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.leyou.com;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
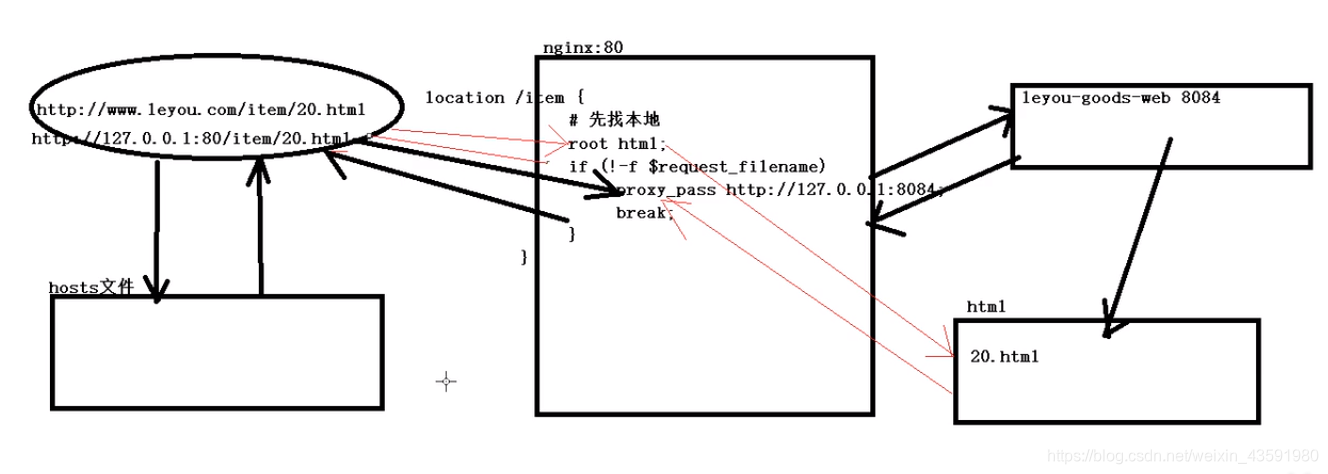
location /item {
root html;
if (!-f $request_filename) {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8084;
break;
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9002;
proxy_connect_timeout 600;
proxy_read_timeout 600;
}
}
|
nginx 代理的流程图:
6. 访问页面测试
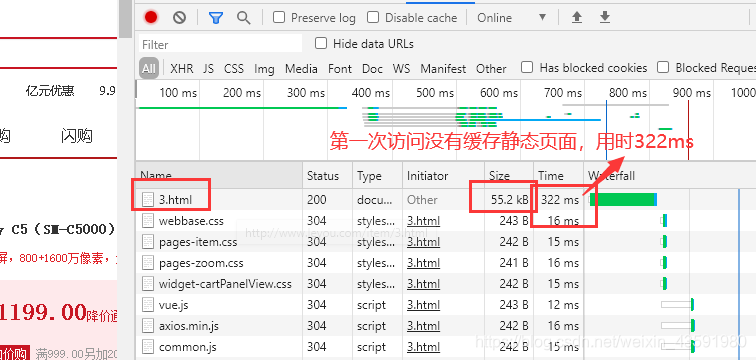
第一次访问页面:
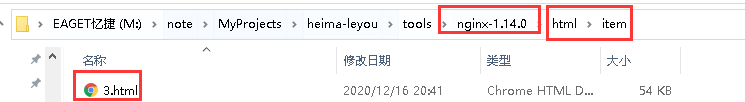
nginx路径下的html/item/下生成了该页面的静态资源:
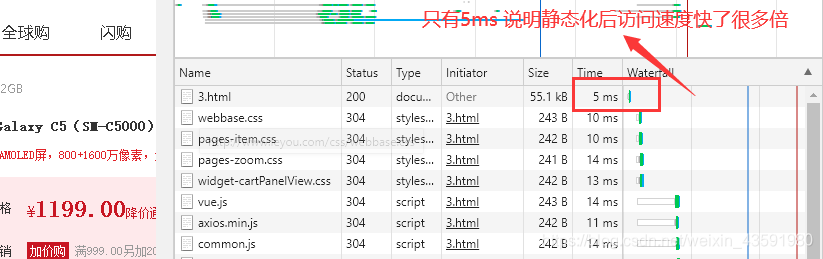
第二次访问该页面: